Written By: Don Dodi
Fact Checked By: Kristen Brown
Reviewed By: Diego Rosenberg
Yes, a Central Locking System is security features which is available on the modern cars and these are actually designed to Lock & Unlock all doors at the same time with the help of pressing a button or by turning of a key.
And it is first introduced in the 1980s and from then it become a standard feature in nearly every vehicle, as it actually provides safety and convenience to the driver and passengers.
Also, according to the automotive repair data: the Door Lock Actuators: which are tiny electric motors that drives the locking mechanism, so these are among the most common parts to fail in vehicles after 6 to 10 years of use.
As well as, the problem with central locking could be anything from weak key fob battery or a blown fuse or there can be more complex issues as well such as: broken wiring inside the door hinge or a faulty actuator can also trigger this problem.
Now, this guide is dedicated on How to Fix Central Locking System, so that can prevent the significant repair costs and this will also prevent the frustration of being locked out or left with a car that actually won’t secure properly.
Ensure About Safety and Preparation
Before you begin repairing your car’s central locking system, it’s important to understand the importance of safety and preparation.
Working with a vehicle’s electronics can be risky if proper precautions are not taken and mistakes can lead to short circuits, damage to the locking system, or even personal injury.
Making sure you’re working in a safe and well-lit environment is the first step.
Park your car on a level surface and apply the parking brake so the car doesn’t move suddenly while you’re working.
Avoid working on busy roads or slopes to minimize risks.
Taking a few minutes to prepare your workspace will make the repair process easier and safer, allowing you to focus solely on fixing the central locking system.
1. Park Safely and Disconnect the Battery
One of the most important steps in repairing a central locking system is disconnecting the car’s battery.
The central locking system is powered by the vehicle’s electrical system and leaving the battery connected could result in a risk of electrical shock or short circuits when handling wires, actuators or switches.
Before beginning any work, turn off the ignition and remove the keys.
Locate the battery, which is usually in the engine compartment and carefully disconnect the negative terminal first and then the positive terminal.
This prevents accidental sparks and ensures that electricity does not flow through the door locking circuits while inspecting or replacing parts.
Disconnecting the battery also protects the vehicle’s electronic control modules from accidental damage, which can occur when electrical wires touch or metal tools hit the battery terminals.
2. Required Tools and Materials
Having the right tools and materials ready is essential to completing repairs efficiently and correctly.
For diagnosing and repairing a central locking system, some of the most useful tools include a multimeter for checking electrical continuity and voltage, screwdrivers for removing door panels and interior trim and special trim tools to prevent damage to plastic clips and panels.
Replacement parts such as fuses, relays, key-fob batteries or door lock actuators should be available to avoid interruptions in the repair process.
Other useful items include contact cleaner for cleaning corroded connectors, dielectric grease to protect electrical connections and small pliers for handling wires or clips.
Having all tools and materials ready before starting work ensures that you can follow the repair steps methodically, make fewer mistakes and reduce the risk of further damaging the central locking system.
Checks Before Going for the Fix
Before starting complex repairs, it’s important to perform a preliminary check to identify the most common and easily fixable problems in the central locking system.
Many malfunctions are caused by simple problems that can be fixed quickly, saving both time and money.
These preliminary checks provide a clear start and help narrow down the cause of the problem.
1. Check the key fob battery and replace if needed
One of the most common reasons a central locking system stops working is a weak or worn key fob battery.
The key fob communicates with the car’s locking system via a radio signal and if the battery is low, the signal may be too weak to activate the locks.
To check the battery, see if the lock or unlock button on the key fob is causing any response from the car, such as flashing lights or the sound of the actuator.
If there is no response or very little response, replace the battery with the correct type of battery, usually a small coin cell battery such as a CR2032.
After replacing the battery, test the fob again to make sure it is sending signals properly.
This simple step resolves many central locking problems without any additional electrical inspection.
2. Check the manual door locks and switches
Next, inspect the manual door locks and interior switches to make sure they are working properly.
Sometimes, the problem may be mechanical rather than electrical, such as a lock jammed or a switch stuck.
Operate each door lock manually and press the interior lock/unlock switch while listening for the actuators to move.
If a door does not respond to the switch, this may indicate a faulty actuator or a wiring problem associated with that specific door.
This step helps determine if the problem is limited to just one door or affects the entire central locking system.
3. Inspect the fuses and relays related to the locking system
Fuses and relays are designed to protect the central locking circuits from electrical damage.
A blown fuse or faulty relay can prevent power from reaching the system, causing all locks to fail.
Locate the fuse box, which is usually located under the dashboard or in the engine compartment and check the fuses related to the central locking system.
Check for any obvious signs of a blown fuse or use a multimeter to check for continuity.
Relays can be checked by placing a similar relay in the fuse box or using a multimeter to check for proper operation.
Ensuring the safety of fuses and relays is an important step in diagnosing central locking failures, as replacing a blown fuse or faulty relay can restore the system immediately.
How to Diagnose the problem
After the initial checks are complete, the next step is to diagnose the underlying problem in the central locking system.
An accurate diagnosis helps identify whether the problem is simple or requires more technical intervention.
This step involves checking each door, listening for mechanical sounds, testing the electrical connections and inspecting for damage in the wiring.
A systematic approach ensures that you do not overlook minor faults that may affect the entire system.
1. Determine if all doors are affected or just one
The first diagnostic step is to see if the central locking problem affects all doors or just one.
If all doors fail to lock or unlock, the problem is probably related to a power supply problem, blown fuse, faulty relay, or a problem in the central control module.
If only one door is not responding, the problem is probably mechanical or electrical in that specific door, such as a faulty actuator, broken linkage, or damaged wire.
Identifying whether the problem is systemic or isolated narrows down the possible causes and saves time during repairs.
2. Listen to actuator sounds inside the doors
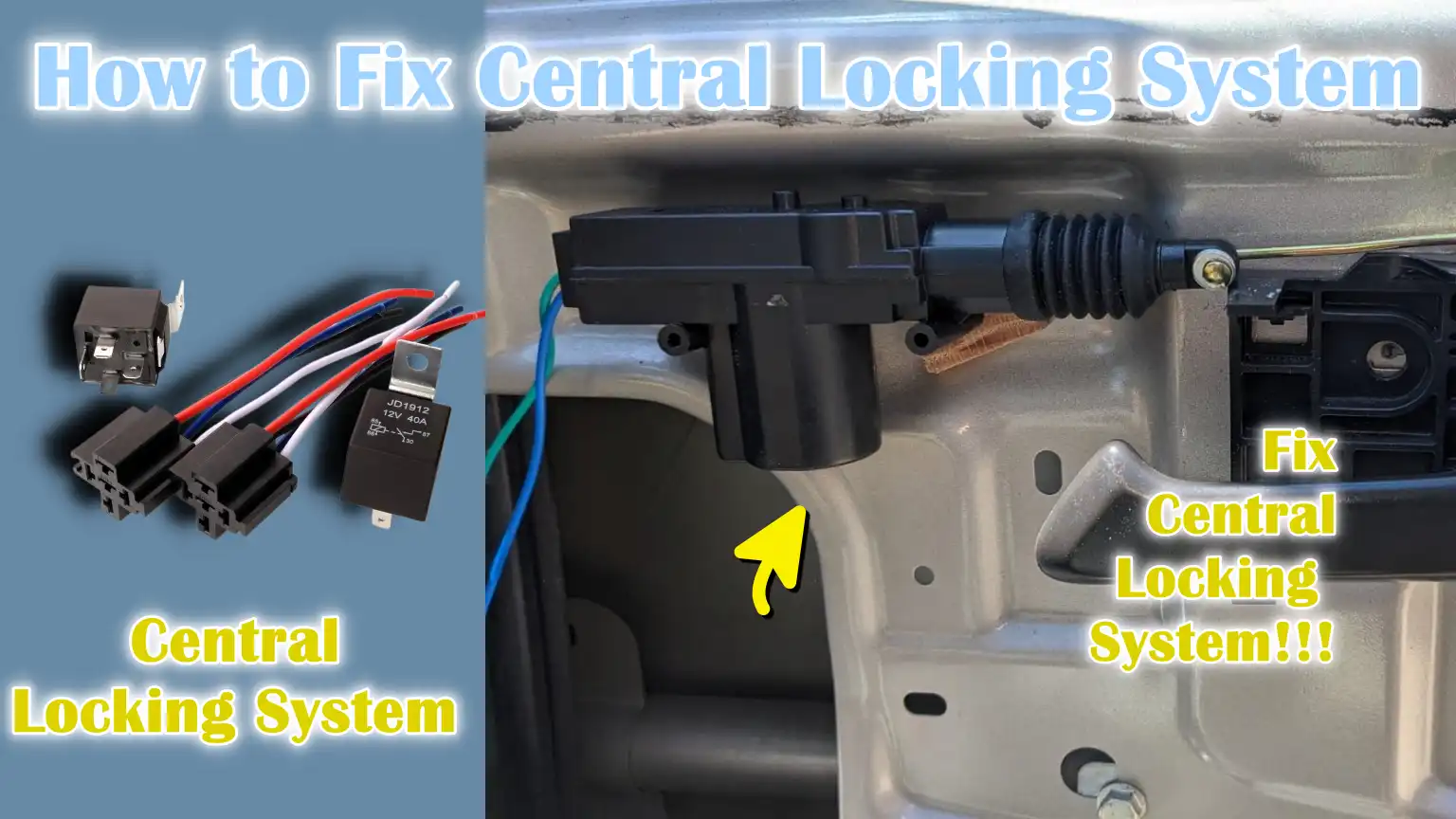
Door lock actuators are small electric motors that are responsible for physically operating the locking mechanism.
When diagnosing a central locking system, it is important to listen carefully for any sounds when pressing the lock or unlock button.
Clicking or humming sounds usually indicate that the actuator is receiving a signal, but it may be weak or partially jammed.
Complete silence indicates that the actuator is not receiving power or is completely out of order.
By paying attention to these sounds, you can figure out which doors are working and which doors need further inspection or replacement.
3. Use a multimeter to check for power and ground in the actuator
A multimeter is an essential tool for diagnosing electrical problems in a central locking system.
Checking power and ground at each actuator helps confirm whether the actuator is receiving the necessary electrical signals.
To do this, set a multimeter to measure voltage and check the wires connected to the actuator while pressing the lock or unlock button.
If voltage is present but the actuator is not working, it is probably defective.
If voltage is absent, the problem may be in the wiring, switch, fuse, or relay.
Accurate electrical testing prevents unnecessary replacement of working parts and ensures that the root cause is correctly identified.
4. Check the wiring around the door hinges and connectors for wear or corrosion
The wiring around the door is constantly in motion as the door opens and closes, making it susceptible to wear, tear, or corrosion over time.
It is important to inspect the wiring harness inside the door hinges, connectors and rubber boots to identify hidden faults.
Check for exposed wires, worn insulation or green corrosion on connectors, as these can disrupt the electrical signals sent to the actuators.
Repairing damaged wiring or cleaning corroded connectors can often get the central locking system working normally without replacing major components.
How to Troubleshooting Common Problems
After diagnosing the central locking system, many common problems that frequently occur in vehicles can be resolved.
These problems are often easy to fix, but they have a profound impact on the system’s functionality.
By following a step-by-step approach, even beginners can understand the cause of the problem and help the system function properly.
1. Replace a Dead Key Fob Battery
A dead or weak key fob battery is one of the most common causes of central locking failure.
The key fob communicates with the car’s locking system via radio signals and if the battery is low, the signal may be too weak to trigger the actuators.
To fix this, carefully open the key fob case and replace the old battery with the correct type of battery, usually a CR2032 coin cell or a model-specific replacement.
After installing the new battery, test the key fob to ensure it is sending signals properly.
Regularly checking and replacing key fob batteries can prevent future locking problems.
2. How to Replace a Bad or Blown Relay
Fuses and relays protect the central locking circuit from electrical overload.
Bad or blown relays can disrupt the system’s power supply, causing the system to stop working.
Locate the fuse box and identify the fuse or relay responsible for the central locking system.
If a fuse is blown, replace it with a fuse or relay with the same amperage rating.
Relays can often be tested by installing a similar relay in the fuse box or checking for continuity and proper operation using a multimeter.
Replacing a bad or blown relay usually restores the central locking system to full function immediately.
3. Repair or Replace Broken Wires/Connectors
Electrical wires around doors can fray, break, or rust over time, specially around hinges and moving parts.
Check the wiring for worn insulation, broken wires, or corroded connectors.
Minor damage can often be repaired by stripping the wire ends, reconnecting them and securing the connection with solder and heat-shrink tubing or properly insulated crimp connectors.
Severely damaged wiring may require complete replacement of the affected part.
Ensuring that all connectors are clean, properly seated and corrosion-free helps maintain reliable electrical contact and restore central locking.
4. Replace a faulty actuator inside the door
The door lock actuator is a small electric motor that physically drives the lock mechanism.
A faulty actuator will prevent the door from locking or unlocking even if the electrical signal is correct.
To replace it, carefully remove the panel inside the door to access the actuator and disconnect its electrical connector and mechanical linkage.
Install the new actuator in the correct position, reconnect the linkage and test its operation before reassembling the door panel.
Using the proper replacement actuator designed for your vehicle ensures smooth operation and long-term reliability.
5. Lubricate the Linkage and Moving Parts
Mechanical linkages and moving parts inside the door can wear out, jam, or become stiff due to dust, dirt, or lack of lubrication.
Applying a suitable lubricant, such as white lithium grease, to the actuator linkage, lock rod and hinges reduces friction and ensures smooth operation.
Regular lubrication not only improves performance but also extends the lifespan of the central locking system.
Avoid excessive lubrication, as excess grease can attract dirt and cause future problems.
Proper linkage maintenance is a simple yet highly effective way to prevent recurring problems.
How to Do Reassembly and Testing
After repairing or replacing central locking system components, it is important to carefully reassemble the doors and test the system to ensure it is fully functional.
Proper reassembly and testing ensure that all repairs were successful and that no damage was caused during the repair process.
Following these steps prevents future malfunctions and maintains the safety and comfort of your vehicle.
1. Refit Door Panels and Reconnect Switches
After all repairs, replacements, or adjustments inside the doors are complete, the interior panels must be carefully reassembled.
First, align the door panels correctly and ensure that all clips and fasteners are securely in place.
Reconnect any switches, wiring harnesses, or connectors that were disconnected during the repair.
Ensuring proper alignment and secure attachment of the door panels can prevent rattling, accidental connections and disruption of the lock mechanism.
This step restores the car’s interior to its original condition while also keeping the central locking components safe and fully functional.
2. Reconnect the Battery
After completing the reassembly, it’s important to reconnect the car’s battery to restore power to the central locking system and other electronic components.
Reconnect the positive terminal first, followed by the negative terminal, ensuring that the connections are strong and corrosion-free.
Reconnecting the battery restores the electrical system to normal operation and allows you to test the lock’s functionality.
Always exercise caution when handling the battery to avoid sparks or accidental short circuits, as this ensures both personal safety and the safety of the vehicle’s electronic modules.
3. Test the Central Locking with Both the Key Fob and Door Switch
After reconnecting the battery, it’s important to thoroughly test the central locking system.
Operate the lock using both the key fob and the interior door switch to ensure that each door locks and unlocks smoothly.
Pay attention to the movement and sound of the actuators, ensuring that all doors are operating in the same manner.
Testing each door individually helps identify any remaining problems with the wiring, actuators, or switches.
This final verification ensures that the central locking system is fully functional, reliable and safe to use on a daily basis.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many central locking problems can be fixed with basic tools and simple troubleshooting, some require the expertise of a professional mechanic or automotive electrician.
It’s important to know when to seek help to avoid further damage, compromising vehicle safety, or wasting time on repairs that can’t be easily performed at home.
Understanding the limitations of self-repair ensures the system is properly restored and continues to function reliably over time.
1. If the Problem Is Related to the Central Locking ECU/Module
The central locking system in modern vehicles is controlled by an electronic control unit, often called an ECU or module.
This component coordinates signals from the key fob, door switches and actuators to ensure all locks work in unison.
If the ECU or module malfunctions, the entire system may malfunction intermittently or stop working altogether.
Repairing or replacing an ECU requires specialized knowledge, diagnostic equipment and sometimes programming.
Attempting to repair the ECU without the proper tools can cause permanent damage to the car’s electronic components, making professional assistance necessary.
2. If Reprogramming Is Necessary
Some central locking systems, specially in newer vehicles, may require reprogramming after replacing components such as the key fob, door actuator, or ECU.
Reprogramming ensures that the key fob and module communicate correctly and all doors function as expected.
This process typically involves specialized diagnostic equipment and software that is not available to the general public.
Incorrect programming can cause inconsistent operation, system errors, or even a completely inoperative locking system.
A trained professional can perform reprogramming safely and accurately.
3. If Electrical Diagnosis Gets Too Complicated
Sometimes, central locking failures are caused by complex electrical problems, including hidden wire breaks, short circuits, or intermittent connectivity issues in the vehicle’s wiring harness.
Diagnosing these problems requires advanced skills, specialized equipment such as scan tools and multimeters and an understanding of automotive electrical systems.
Attempting complex electrical repairs without experience can lead to misdiagnosis, further damage, or even a safety hazard.
In such cases, consulting a professional ensures that the root cause is identified and corrected correctly, restoring reliable operation of the central locking system.
Read More:
Basic Tips to Prevent It From Happen

Proper maintenance of the central locking system can prevent most common problems and extend the system’s life.
Small, regular maintenance steps help ensure locks function smoothly, reduce repair costs and maintain the safety and convenience of your vehicle.
By following a few simple steps, car owners can avoid many problems that often arise due to neglect or environmental factors.
Plus, the investigation of NHTSA about alleged malfunctions of electric powered door locks that shows that there are basic symptoms patterns are available and it is true that components such as: actuators, wiring and connectors corrosion are recurring causes of door-lock failures: and yes it is the common real-world failure modes and that’s why it is really important to diagnose these parts first.[¹]
1. Regularly Replace Key Fob Batteries
The key fob is the primary device used to remotely operate the central locking system and a weak or dead battery is one of the leading causes of failure.
Even if the key fob appears to be working intermittently, replacing the battery every one to two years or when signs of weakness appear can prevent sudden malfunctions.
Using the correct type of battery ensures proper voltage and reliable signal transmission to the car’s locking system.
Regularly replacing the battery keeps the key fob functional and avoids unnecessary troubleshooting for potential system failures.
2. Maintain Door Seals to Prevent Water Damage
Door seals play a vital role in protecting the central locking system’s electrical components from moisture and dirt.
Damaged or worn seals can allow water to enter the door cavity, causing corrosion of the actuator, wires and connectors.
Periodically inspect the seals for cracks, gaps, or hardening and replace them if necessary.
Keeping the seals intact prevents moisture-related failures, reduces the risk of electrical short circuits and keeps the lock’s mechanical components running smoothly over time.
3. Periodically Lubricate the Door Lock Mechanism
Over time, the mechanical linkages inside the door can become stiff due to dirt, dust, or lack of lubrication.
Applying a suitable lubricant, such as white lithium grease, to the lock rod, actuator linkage and door mechanism reduces friction and ensures smooth operation.
Regular lubrication prevents excessive wear on the actuators and reduces the likelihood of mechanical failure.
This simple maintenance step keeps the central locking system responsive and helps extend the overall lifespan of both electrical and mechanical components.
4. Inspect the Wiring Harness During Routine Maintenance
The wiring harness connecting the central locking system components is susceptible to wear, specially near the door hinges where wires are often bent.
Periodically inspect the wiring for fraying, broken insulation, or corrosion in the connectors.
Early detection of wiring problems allows them to be fixed before the lock fails completely.
Maintaining clean and intact wiring ensures the continuous flow of electrical signals to all actuators and switches, increasing reliability and preventing unexpected malfunctions.
Conclusion – How to Fix Central Locking System
The maintenance is all about having convenient central locking system and when you take care of batteries, fuses, actuators and wiring at the regular time interval: that not only fixes this problem easily but also it literally enhances the overall reliability and safety of your vehicle as well.
Most problems stem from simple causes, such as a weak key fob battery, a blown fuse, a faulty relay, or a worn actuator and can be completely fixed with a complete overhaul without professional assistance.
Proper diagnosis involves checking whether all doors are affected or just one, listening to the actuator, testing the power and ground at the actuator and inspecting for damage or corrosion in the wiring.
Once the root cause is identified, repairs such as replacing the battery, fuse, relay, actuator, or wiring and lubricating the linkage ensure smooth operation.
Safety and preparation, including disconnecting the battery and using the correct tools, are essential to prevent damage and ensure personal safety during repairs.
While some serious problems, such as ECU malfunctions, reprogramming, or complex electrical failures, require professional assistance, adopting a structured approach allows most car owners to efficiently troubleshoot and repair their central locking system.
Additionally, preventative maintenance such as regular battery replacement, door seal protection, mechanism lubrication and wiring inspection can extend the system’s lifespan and prevent unexpected failures.
So, you can now comment down below if you wanted more information specifically.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is a central locking system and how does it work?
Answer: The central locking system is an electronic or electromechanical system installed in a car that allows all doors to be locked or unlocked simultaneously. It sends signals to the central control unit or directly to the door actuators using a key fob, remote control, or manual switch inside the car. These actuators are small motors inside each door that drive the locking mechanism. When the system receives a signal, it activates all door actuators, allowing the doors to lock or unlock simultaneously. This system provides convenience, increases vehicle security and ensures that all doors are secured quickly and simultaneously.
Q2. Why is my central locking system not working properly?
Answer: There are several common reasons why the central locking system may stop working. One of the most common causes is a weak or defective key fob battery, which prevents the signal from reaching the car’s locks. Another common problem is a blown fuse or a faulty relay that disrupts the system’s power supply. Door lock actuators can also wear out over time, causing one or all doors to fail. Wiring problems, such as breaks, corrosion, or loose connectors, are another cause of malfunction, specially in areas with frequent movement, such as door hinges. Knowing the exact cause helps choose the right repair method.
Q3. Can I fix my central locking system myself at home?
Answer: Yes, many central locking problems can be fixed at home using basic tools and a step-by-step process. Simple problems like replacing the key fob battery, replacing a fuse, replacing a faulty relay, or lubricating the mechanical linkages inside the doors can often be fixed by car owners without professional help. More complex problems, such as broken wiring in the door harness or a faulty ECU/module, may require professional expertise, but performing initial inspections and basic repairs at home can save time and money. Proper safety precautions, such as disconnecting the battery and using the correct tools, are essential to avoid damage.
Q4. How do I know if a door lock actuator is bad?
Answer: A bad door lock actuator usually shows specific symptoms. If a door won’t lock or unlock while other doors are functioning normally, that door’s actuator may be faulty. You may hear a clicking or humming sound when you press the lock or unlock button, or if the actuator is completely locked, you may hear nothing at all. Testing the actuator with a multimeter for power and ground can confirm whether it is receiving signals. If it’s receiving power but not moving, the actuator may be faulty and needs to be replaced. Replacing a faulty actuator often restores full functionality to the central locking system.
Q5. What maintenance can be performed to prevent future central locking problems?
Answer: Regular maintenance plays a vital role in preventing central locking problems. Replacing key fob batteries periodically ensures that signals continue to reach the system. Keeping door seals intact prevents water or moisture from entering the door cavity and corroding electrical components. Lubricating the door lock linkage and moving parts reduces friction and wear on the actuator and rod. Inspecting the wiring harness, specially near hinges where wires are frequently bent, helps detect wear or corrosion before it causes a malfunction. Following these simple maintenance steps increases reliability and extends the lifespan of the central locking system.
Q6. When should I call a professional mechanic?
Answer: When the problem is related to the central locking ECU or module, when reprogramming is required after replacing parts, or when electrical problems are too complex to safely diagnose at home, a professional mechanic should be consulted. Attempting to fix advanced electronic or wiring problems without the proper tools and experience can cause further damage or safety risks. Professionals have specialized diagnostic equipment and knowledge to identify hidden faults and safely reprogram or replace modules. Calling a professional ensures that the system is restored correctly and reliably.
Q7. Will replacing the key fob battery fix all central locking problems?
Answer: Replacing the key fob battery can solve many central locking problems, but not all. If the key fob is weak or dead, the system may not receive a signal and replacing the battery usually fixes the problem. However, if the problem is caused by a blown fuse, a faulty relay, broken wiring, or a worn actuator, simply replacing the battery will not restore its functionality. Before assuming that replacing the battery will solve the problem, it’s important to test the system and determine the exact cause.
References:
[1] Malfunction of Electric Powered Door Locks In Model Year 2001 Kia Optima Vehicles
https://static.nhtsa.gov/odi/inv/2004/INCR-EA04030-22746P.pdf

Guys, I’m a car audio enthusiast and customization expert and I love clear sound and clean installation. Plus, I have spent years helping people build their dream audio setups. And whenever I’m working on cars, I probably listen to music and thinks about the next big upgrade.