Written By: Don Dodi
Fact Checked By: Kristen Brown
Reviewed By: Diego Rosenberg
Basically, a second battery gives your vehicle the extra power without risking the battery to be a dead starter when you need to drive.
Now-a-days, modern cars often run with the additional equipments such as: dash cams, refrigerators, powerful audio systems, auxiliary lights, work tools and camping gears as well; and these are all the things that demands heavy power from the electrical system.
That’s why, a single starter battery is not capable of doing all these kinds of things, because a single starter battery is actually designed to start the ending, not to the power accessories for long periods of tie.
Additionally, when there are too many devices that tends to draw the power from the main battery, then it is easy for the battery to drain out quickly and that leave the vehicle unable to start after all.
So, the perfect solution to all these problems is: A Second Battery; as it provides a dedicated power source that runs accessories separately and that’s how it also protects the main battery from unexpected loads and dangerous deep drainage.
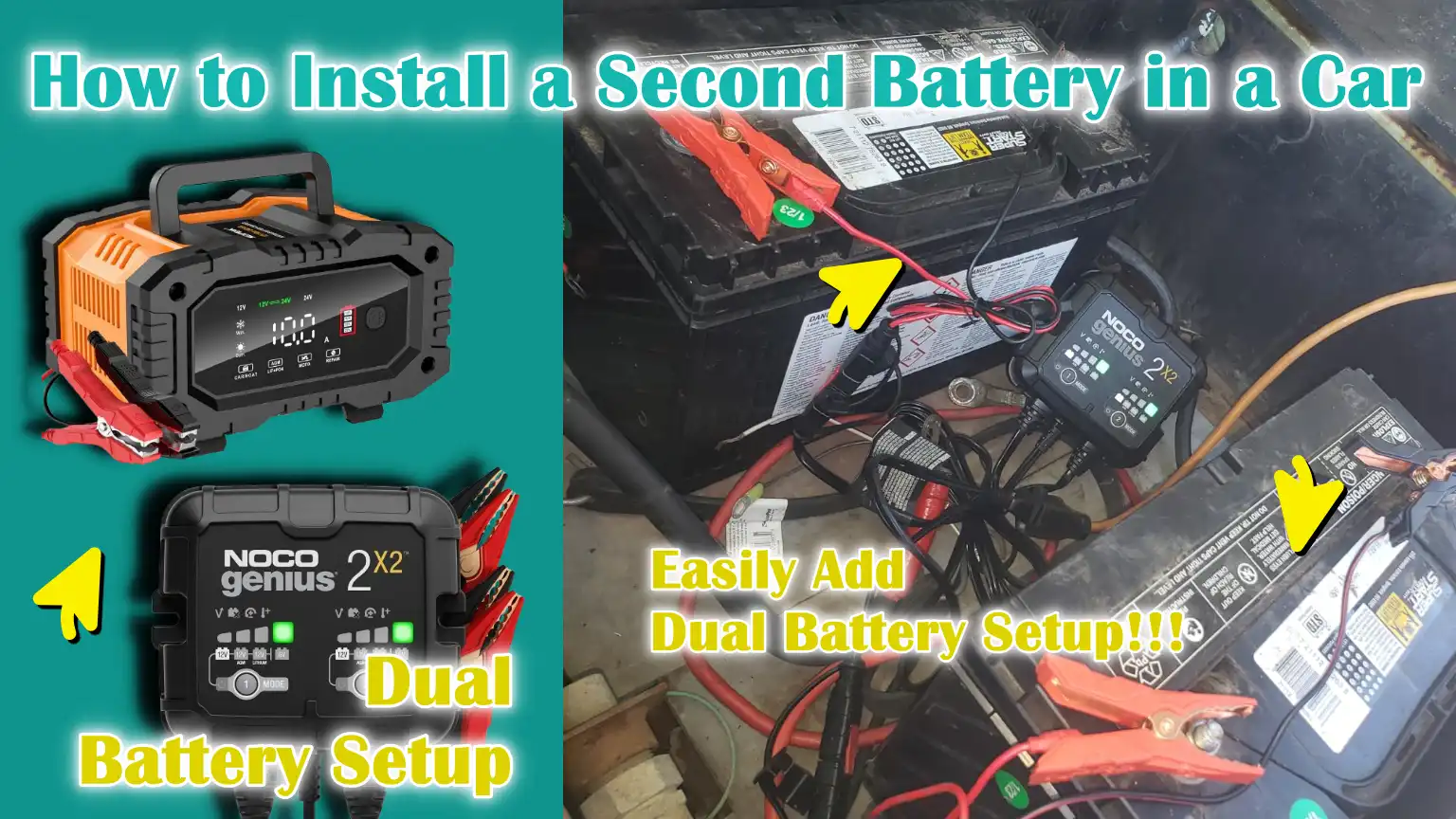
Now, we have come up with this guide on How to Install a Second Battery in a Car, so that you can understand about proper wiring, fuses and battery isolator or DC to DC charger, as the dual battery setup literally allows the both the batteries to charge safely while the engine is running and that prevents the power loss when the engine is off as well.
Moreover, it overall improves the reliability, reduces the electrical strain and ensures very consistent power availability so that you can go for the off-road adventures, camping or for the long family vacation.
What are the Benefits of Installing a Second Battery
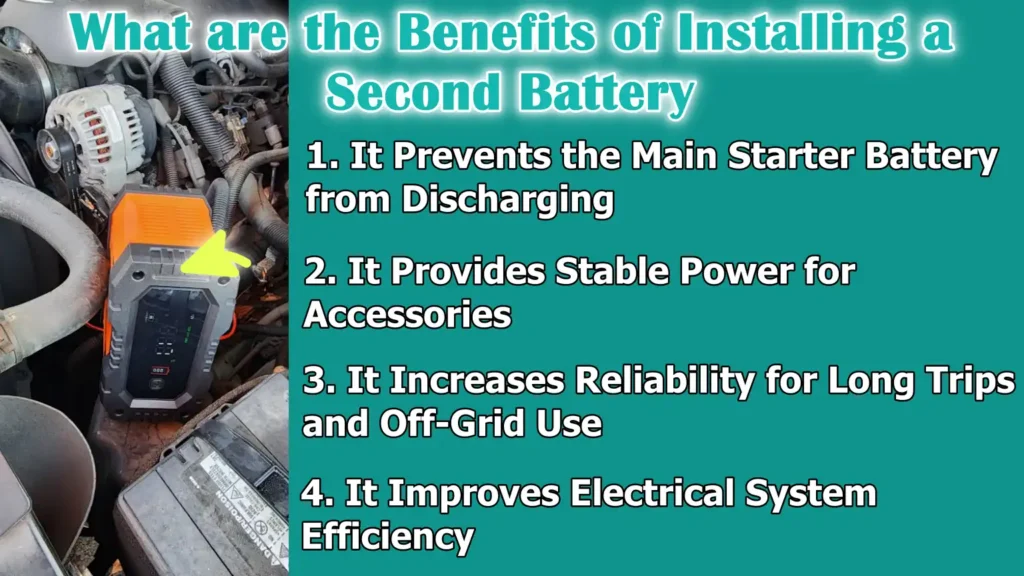
1. It Prevents the Main Starter Battery from Discharging
The biggest advantage of installing a second battery is that it prevents the main starter battery from discharging.
The starter battery in a car is primarily designed to start the engine, not to power electrical accessories for extended periods.
When devices like dash cams, lights, sound systems, refrigerators, or chargers draw power from the main battery, it can quickly discharge, specially when the engine is off.
The second battery takes over the task of powering these accessories, leaving the starter battery fully charged and ready to start the engine at any time.
This significantly reduces the risk of being stranded due to a dead battery.
2. It Provides Stable Power for Accessories
A second battery provides a stable and reliable power supply for electrical accessories.
Many car accessories require a consistent voltage to function correctly and sudden drops in power can cause devices to shut down, reset, or malfunction.
With a dedicated auxiliary battery, accessories receive clean and stable power without interruption.
This is specially helpful for devices that run continuously, such as camping refrigerators, navigation systems, communication devices, or work equipment.
Stable power also helps prevent damage to sensitive electronics caused by voltage fluctuations.
3. It Increases Reliability for Long Trips and Off-Grid Use
Installing a second battery greatly increases the reliability of your vehicle during long trips and off-grid situations.
When you’re traveling far from cities, campsites, or repair facilities, reliable power becomes crucial.
A dual battery system allows drivers to use lights, fans, charging ports and other devices for extended periods without worrying about being able to start the engine later.
This setup is widely trusted by off-road drivers, campers and work vehicle owners because it ensures power is available even when the vehicle is parked for several hours or overnight.
4. It Improves Electrical System Efficiency
A properly installed second battery helps the vehicle’s electrical system operate more efficiently.
By separating the engine-starting function from the accessory power usage, the electrical load is distributed more evenly.
This reduces stress on the alternator, wiring and main battery.
When used with a battery isolator or DC-DC charger, both batteries charge safely and correctly while the engine is running, without overcharging or power loss.
Over time, this balanced system can extend battery life, reduce electrical problems and maintain overall better performance.
Now, Let’s Understand When a Second Battery is Needed
1. High-Power Accessories That Require More Energy
A second battery becomes necessary when a vehicle uses accessories that require more electrical energy than a standard starter battery can provide.
High-power devices such as amplifiers, subwoofers, off-road lights, winches, refrigerators, inverters, air compressors and multiple charging ports draw power continuously or in large bursts.
These accessories are not designed to rely on the starter battery, which is only intended to provide a short burst of high power for starting the engine.
When such equipment runs for extended periods, specially with the engine off, the main battery discharges rapidly.
A second battery is designed to handle this continuous load, making it a safer and more reliable power source for high-energy accessories.
2. Signs of an Overloaded Electrical System
There are several clear indicators that a vehicle’s electrical system may be overloaded and requires a second battery.
Common signs include dimming headlights when accessories are turned on, slow engine cranking, frequent dead battery issues, warning lights on the dashboard and accessories suddenly shutting off.
In some cases, wires may feel hot, fuses may blow frequently, or the alternator may seem to struggle to keep up with power demands.
These symptoms suggest that too much electrical load is being placed on a single battery and charging system.
Adding a second battery distributes the load and protects the battery, alternator and wiring from long-term damage.
3. Daily Driving vs Recreational or Commercial Use
The need for a second battery often depends on how the vehicle is used.
For normal daily driving with factory-installed electronics, one battery is usually sufficient.
However, recreational vehicles such as camper vans, off-road SUVs and overlanding setups often rely on power for extended periods, even when the engine is off.
Commercial vehicles used for mobile offices, delivery services, emergency response, or construction work also power multiple devices throughout the day.
In these situations, a second battery ensures uninterrupted power while maintaining the ability to start the engine.
Vehicles used for more than just general transportation benefit most from a dual battery system.
4. Legal and Manufacturer Considerations
Before installing a second battery, it’s crucial to consider legal requirements and manufacturer guidelines.
Some vehicles have limited space, specific electrical layouts, or sensitive electronic systems that require approved installation methods.
Incorrect wiring can void warranties or cause electrical malfunctions.
In some jurisdictions, safety or inspection regulations may apply to battery installations, ventilation and secure mounting in commercial or modified vehicles.
Using manufacturer-recommended components, proper fusing and professional installation standards ensures compliance, safety and long-term reliability.
Now, Understand What are the Other Battery Types That You Can Use
1. Deep – Cycle Batteries
Deep-cycle batteries are one of the most common options for auxiliary batteries because they are designed to provide a continuous power supply over a long period of time.
Unlike starter batteries, which provide power for a short period of time to start the engine, deep-cycle batteries are designed to withstand repeated discharge and recharge cycles without damage.
This makes them ideal for powering accessories like refrigerators, lights, fans and inverters for many hours.
Deep-cycle batteries are commonly used in campervans, boats and off-road vehicles because they are reliable and economical.
However, they are generally heavier than some modern battery types and charge slowly, which is an important consideration when choosing the right setup.
2. AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) Batteries
AGM batteries are a more advanced type of lead-acid battery and are widely used as auxiliary batteries in modern vehicles.
They store energy in a fiberglass mat, making them spill-proof and safer to install in confined spaces like the trunk or under seats.
AGM batteries charge faster than traditional deep-cycle batteries and provide a stable voltage, which is crucial for sensitive electronics.
They also handle vibration well, making them ideal for off-road and work vehicles.
Although AGM batteries are more expensive than standard deep-cycle batteries, they last longer and require much less maintenance, making them a popular choice for dual battery systems.
3. Lithium Batteries
Lithium batteries are the newest and most efficient option for auxiliary battery systems.
They are much lighter than lead-acid batteries and can store more usable energy in a smaller size.
Lithium batteries can be fully discharged without losing performance and charge very quickly when paired with the right charging system.
This makes them ideal for long trips, camping and high-power setups.
However, lithium batteries are more expensive and require a compatible DC-DC charger to ensure safe charging.
When installed correctly, they offer longer life, better efficiency and consistent power output compared to traditional battery types.
4. Matching Battery Types vs Combining Different Batteries
Choosing whether to match or mix battery types in a dual battery system is an important decision.
Using the same battery type for both the main and auxiliary batteries ensures consistent charging behavior and reduces the risk of electrical imbalance.
Mixing different battery types, such as a starter battery with a lithium or AGM auxiliary battery, can work, but requires proper isolation and charging control.
Without the right equipment, different battery types can charge unevenly or cause premature failure.
Using a battery isolator or DC-DC charger helps manage the differences in voltage and charging requirements, making mixed setups safe and reliable when done correctly.
Tools
| Component | Simple Explanation |
|---|---|
| Second Battery | This is an auxiliary battery that powers accessories such as lights, refrigerators, or audio systems. It operates independently of the main battery, so the engine’s battery doesn’t get discharged. |
| Battery Tray | The battery tray securely holds the second battery in place. This prevents movement, vibration and damage when driving on rough roads. |
| Battery Isolator or DC-DC Charger | This device keeps the main and auxiliary batteries separate. It allows both batteries to charge safely, while also preventing the auxiliary battery from discharging the starter battery. |
| Heavy-Gauge Wiring and Connectors | Thicker wires are needed to safely carry higher electrical power. Robust connectors ensure tight and secure electrical connections. |
| Fuses, Fuse Holders and Circuit Breakers | These devices protect the system from short circuits and overloads. If something goes wrong, they immediately cut off the power, preventing fires or damage. |
| Mounting Hardware | Bolts, brackets and clamps are used to secure all the parts properly. The sturdy mounting keeps the components safe during vibrations and sudden movements. |
| Protective Covers | These covers protect the battery terminals and wires from dust, moisture and accidental contact. This improves safety and reduces corrosion over time. |
How to Choose the Best Location for the Second Battery
1. Engine Bay Installation
Installing a second battery in the engine bay is one of the most common and convenient options.
This location keeps the battery close to the alternator, allowing for efficient charging and minimizing the need for long wiring runs.
Shorter wires mean less power loss and a reduced chance of voltage drop.
Engine bay installation also makes battery inspection and maintenance easier.
However, engine bays can get very hot, specially in modern vehicles.
Excessive heat can shorten battery life, so heat-resistant batteries like AGM or lithium are often preferred for this location.
Proper mounting and secure insulation are crucial to prevent damage from engine vibrations and heat.
2. Trunk or Cargo Area Installation
For vehicles with limited space in the engine bay, installing a second battery in the trunk or cargo area is a popular alternative.
This location offers better protection from engine heat and allows for securely mounting larger or heavier batteries.
Trunk installations are common in camper vans, SUVs and vehicles with large audio systems.
Because the battery is further from the engine, thicker cables are required to ensure proper power flow and safe charging.
Adequate ventilation is also essential, specially for lead-acid batteries, to prevent gas buildup.
When installed correctly, this location provides a clean and organized setup.
3. Under-Seat or Custom Mounting Options
Under-seat or custom mounting options are useful when space is limited or when a hidden installation is preferred.
Many modern vehicles have space under the seats or in custom compartments where a second battery can be securely installed.
This option helps keep the interior clean while protecting the battery from external damage.
However, careful planning is required to ensure adequate airflow and space for wiring.
Only sealed batteries, such as AGM or lithium, should be used in these locations to avoid safety hazards.
Strong mounting is essential to prevent movement during driving or sudden braking.
4. Considerations for Heat, Ventilation and Accessibility
Heat, ventilation and accessibility are crucial factors when choosing the best location for the battery.
Excessive heat can reduce battery efficiency and lifespan, while poor ventilation can lead to gas buildup in some battery types.
The battery should be placed in a location with adequate airflow and away from direct heat sources.
Accessibility is also important for checking connections, replacing fuses and performing maintenance.
Choosing the right location strikes a balance between safety, ease of access and longevity, ensuring the auxiliary battery operates reliably under all driving conditions.
How to Ensure Safety Before Installing the 2nd Battery
1. Disconnecting the Main Battery
Before beginning any work on the vehicle’s electrical system, it is crucial to disconnect the main battery to prevent electric shock and accidental damage.
The negative terminal should always be disconnected first, as this minimizes the risk of a short circuit if a tool accidentally touches metal parts of the vehicle.
Keeping the battery disconnected prevents accidental sparks, protects sensitive electronics and ensures that no power flows while making connections.
This simple step is one of the most important safety procedures and should never be overlooked.
2. Wearing Safety Gear
Wearing safety gear is essential when working around car batteries and electrical components.
Safety gloves protect hands from acid leaks, sharp edges and heat, while safety glasses protect the eyes from sparks or splashes.
A faulty battery can release harmful gases or corrosive substances, so wearing basic protective equipment reduces the risk of injury.
Wearing appropriate clothing also helps prevent accidental burns or cuts during installation.
3. Avoiding Short Circuits and Sparks
Short circuits occur when electricity flows through an unintended path, often resulting in sparks, overheating, or damage.
To avoid this, tools should be kept away from exposed terminals and wires should never touch metal surfaces without insulation.
Fuses should be installed near the battery to immediately interrupt power in case of a fault.
Working slowly and double-checking connections helps minimize errors that could lead to dangerous sparks or electrical fires.
4. Understanding Polarity and Grounding
Understanding polarity and grounding is critical for safe battery installation.
Every battery has a positive and a negative terminal and reversing these connections can damage electrical components or cause battery failure.
Grounding connects the negative terminal to the vehicle’s metal body, allowing electricity to flow safely through the system.
A clean, secure ground connection ensures proper performance and reduces the risk of overheating, voltage problems, or electrical malfunctions.
How to Install a Second Battery in a Car – Effective Method
Installing a second battery requires careful planning and precise execution to ensure safety, reliability and long-lasting performance.
Each step builds upon the previous one and skipping or rushing any part can lead to electrical problems or battery failure.
Following the correct installation process protects both the vehicle and its electrical components.
How to Mount the Second Battery
Properly mounting the second battery is the foundation of a safe and durable dual battery system.
A poorly mounted battery can shift during driving, potentially damaging cables, causing short circuits, or even damaging the battery itself.
The battery should always be securely fastened before any wiring is done.
1. Securely Installing the Battery Tray
The battery tray should be mounted to a sturdy, flat surface using the correct bolts and brackets.
It is designed to hold the battery in place and prevent movement caused by road vibrations or sudden braking.
A secure tray prevents the battery from tipping, sliding, or putting stress on the terminals.
Using a tray specifically designed for the battery size ensures a proper fit and secure placement.
2. Correctly Positioning the Battery
The battery should be placed upright and properly aligned within the tray.
The terminals should be positioned in a direction that allows for easy wiring without straining or bending the cables.
Correct positioning also ensures the battery remains balanced and does not come into contact with sharp edges or hot components.
Proper positioning improves airflow and makes future inspections or replacements easier.
3. Ensuring Vibration Resistance
Vehicles experience constant vibrations from road and engine movement.
To prevent damage, the battery must be secured with clamps or straps that can absorb these vibrations.
Excessive vibration can loosen connections, crack the battery casing, or reduce battery life.
A vibration-resistant setup ensures stable electrical connections and long-lasting reliability.
How to Install a Battery Isolator or DC to DC Charger
In a dual battery system, an isolation device is crucial because it controls how power flows between the main battery, auxiliary battery and alternator.
Without proper isolation, both batteries can discharge simultaneously, defeating the purpose of the system.
1. Purpose of the Isolation System
The primary purpose of a battery isolator or DC-DC charger is to protect the starter battery.
These devices allow both batteries to charge when the engine is running but prevent accessories from discharging the main battery when the engine is off.
This ensures that the vehicle can always start, even after prolonged use of accessories.
2. Correct Isolator Wiring
The isolator or DC-DC charger must be wired according to the manufacturer’s instructions, with the correct input and output connections.
Power from the main battery or alternator passes through the device before reaching the auxiliary battery.
Correct wiring ensures safe charging, proper voltage regulation and protection against overcharging or reverse current flow.
3. Difference Between Isolators and DC-DC Chargers
Battery isolators are simple devices that connect and disconnect batteries based on voltage levels.
DC-DC chargers actively manage charging by adjusting voltage and current according to the battery type.
DC-DC chargers are particularly important for AGM and lithium batteries, as they provide more precise and efficient charging.
Choosing the right device optimizes battery health and system efficiency.
How to Do Wiring of Second Battery
Wiring is one of the most crucial aspects of installing a second battery.
Proper wiring ensures safe power transfer, minimizes power loss and reduces the risk of overheating or fire.
All connections must be clean, tight and securely fastened.
1. Securely Connecting Positive Terminals
The positive terminal of the second battery should be connected using thick, high-quality cables designed for high current flow.
Secure connections minimize resistance and prevent heat buildup.
All positive connections should be covered to prevent accidental contact with metal parts, which could cause a dangerous short circuit.
2. Proper Grounding Techniques
Grounding connects the negative terminal of the battery to the vehicle’s metal body, allowing electricity to flow safely through the system.
The grounding point should be clean, corrosion-free and securely attached.
Poor grounding can lead to voltage drops, charging problems and poor performance of accessories.
3. Installing Fuses Near the Battery
Fuses should be installed as close to the battery as possible to protect the wiring.
In the event of a short circuit, the fuse will immediately interrupt the power, preventing wire damage or fire.
Using the correct fuse rating is essential to ensure protection without interrupting normal operation.
4. Routing Wires to Avoid Heat and Abrasion
Wires should be routed away from sharp edges, moving parts and high-heat areas such as exhaust components.
Protective sleeves or conduits should be used where wires pass through metal panels.
Proper routing prevents insulation damage, reduces wear and tear over time and improves the overall safety of the system.
How to Connect Accessories to the Second Battery
Once the second battery is installed and wired, accessories should be connected carefully to ensure a stable power supply and prevent overloading.
All accessory connections should be planned according to the battery’s capacity.
1. Safe Accessory Wiring Practices
Accessories should always be connected through the correct terminals and protected circuits.
Direct connections without protection can overload the system or damage equipment.
Clean wiring ensures consistent power delivery and reduces the risk of electrical faults.
2. Using Distribution Blocks
Distribution blocks help organize power connections, allowing multiple accessories to safely draw power from a single source.
They simplify wiring, reduce clutter and make troubleshooting easier.
Proper distribution also ensures a balanced power supply to each accessory.
3. Avoiding Overloading
Every battery has a limited capacity and connecting too many accessories can overload the system.
Power consumption should be calculated to ensure the battery can handle the total load.
Avoiding overloading preserves battery life, prevents overheating and ensures reliable performance over time.
How to Test the Dual Battery System
Testing the dual battery system after installation is crucial for safety, proper charging and reliable performance.
Proper testing ensures both batteries are functioning correctly, accessories are receiving adequate power and the starter battery remains fully protected.
Skipping this step can lead to hidden electrical problems that may surface later and cause battery failure or starting difficulties.
1. Checking Voltage Levels
Checking voltage levels is the first step in testing a dual battery system.
A healthy, fully charged battery typically shows approximately 12.5 to 12.8 volts when the engine is off.
When the engine is running, the voltage should increase, indicating that the alternator is charging the battery.
Depending on the charging system used, both the main and auxiliary batteries should show stable and correct voltage readings.
Significant voltage discrepancies can indicate faulty wiring, loose connections, or charging problems that require attention.
2. Verifying Isolation Between Batteries
Verifying isolation ensures that the auxiliary battery does not discharge the main starter battery when the engine is off.
After turning off the engine, accessories should continue to run from the auxiliary battery, while the main battery’s voltage remains stable.
When the engine is restarted, the isolation system should allow both batteries to charge.
This test confirms that the isolator or DC-DC charger is functioning correctly and protecting the starter battery as intended.
3. Testing Accessory Operation
Testing accessory operation ensures that all connected devices receive stable and reliable power.
Lights, audio systems, refrigerators and other appliances should operate smoothly without flickering, shutting off, or experiencing voltage drops.
Accessories should continue to function even with the engine off, drawing power only from the auxiliary battery.
Correct operation indicates proper wiring and sufficient battery capacity for the installed load.
4. Identifying Wiring or Charging Problems
Identifying wiring or charging problems is the final and most crucial part of system testing.
Signs of problems include hot cables, blown fuses, unstable voltage readings, or a battery that won’t fully charge.
These issues can be caused by loose connections, incorrect wire gauge, poor grounding, or a faulty isolation device.
Carefully inspecting all connections and retesting after making repairs ensures the long-term safety, efficient charging and reliable performance of the dual battery system.
What are Some Common Installation Mistakes to Avoid
Adding a second battery can significantly improve a vehicle’s electrical system, but minor mistakes during installation can compromise performance, reduce battery life, or create safety risks.
Understanding common errors helps prevent electrical failures, charging problems and long-term damage.
Avoiding these mistakes ensures the dual battery system remains reliable and safe.
1. Failure to Install an Isolator
Failing to install a battery isolator is one of the most serious installation mistakes.
Without an isolator or DC-DC charger, both batteries remain connected at all times.
This allows accessories to discharge the main starter battery when the engine is off, potentially preventing the vehicle from starting.
An isolator ensures the starter battery remains protected while the auxiliary battery powers the accessories.
Without proper isolation, the entire purpose of adding a second battery is defeated.
2. Using the Wrong Wire Gauge
Using wires that are too thin for the electrical load can lead to overheating, voltage drop and power loss.
Thin wires struggle to safely carry high currents, potentially causing insulation to melt or even leading to a fire.
Thicker, heavy-gauge wiring allows electricity to flow efficiently and safely between the batteries and accessories.
The correct wire size is crucial for efficient charging and long-term reliability.
3. Poor Grounding
Poor grounding is a common cause of electrical problems in dual battery systems.
A weak or loose ground connection can cause voltage drops, flickering accessories and slow charging.
Ground points should be clean, corrosion-free and securely connected to the vehicle’s metal body.
Proper grounding ensures stable power flow and protects the system from overheating and electrical malfunctions.
4. Mixing incompatible battery types
Mixing incompatible battery types without proper charging control can lead to uneven charging and premature battery failure.
Different batteries have different voltage and charging requirements and forcing them to charge in the same way can damage one or both batteries.
When using different battery types, a DC-DC charger is essential to safely manage the charging process.
Matching battery types or using the correct charging equipment ensures balanced performance and a longer battery lifespan.
How to Maintain Dual Battery Setup
Not only that, there’s research in the Journal of Power Sources that shows that the traditional kinds of single-battery design now-a-days struggles to meet the dual demands of engine starting and powering the modern electrical loads, so when you separate these functions into the dedicated starter and service batteries; then the vehicles literally achieve more reliable engine starts and provides consistent power delivery to the other accessories in the way more effectively that is why there’s a huge value of having a second battery in vehicle.[¹]
Maintaining a dual battery system is crucial for ensuring vehicle reliability and guaranteeing that both batteries perform well over time.
Regular maintenance helps prevent unexpected battery failures, charging problems and electrical issues.
A well-maintained system provides stable power, extended battery life and improved overall safety.
1. Regular Voltage Checks
Regular voltage checks help identify battery health and charging performance issues early.
A healthy battery typically shows a stable voltage when fully charged and the voltage increases when the engine is running.
Performing regular voltage checks allows you to detect weak batteries, poor charging, or wiring problems before they become serious issues.
Simple voltage checks can prevent unexpected failures and extend battery life.
2. Keeping Terminals Clean
Clean battery terminals ensure good electrical contact and efficient power flow.
Over time, dirt, corrosion and moisture can accumulate on the terminals, creating resistance that reduces charging efficiency.
Regularly cleaning the terminals helps maintain strong connections and prevent voltage loss.
Tight and clean terminals also reduce heat buildup and improve overall system safety.
3. Monitoring Charging Performance
In a dual battery setup, it’s essential to monitor how both batteries are charging.
When the engine is running, both batteries should receive proper charging through the isolator or DC-DC charger.
If one battery is charging slowly or not at all, it could indicate a wiring problem or a faulty component.
Consistent charging performance ensures reliable accessory power and protects the starter battery.
4. Battery Life Expectations
Understanding battery life helps set realistic expectations and plan for replacements.
Most lead-acid and AGM batteries last for several years with proper maintenance, while lithium batteries can last even longer due to their superior charge efficiency.
Usage patterns, charging quality and operating temperature all affect battery lifespan.
Regular maintenance and proper charging significantly extend the reliable service life of a battery.
Read More:
Understand About the Cost and Installation Time
Understanding the costs and time involved in installing a second battery allows you to set realistic expectations and avoid surprises.
Costs and installation time depend on the type of battery, vehicle design and whether the work is done at home or by a professional.
Planning ahead ensures the system is efficient and within budget.
1. Common Component Costs
Component costs largely depend on the type of second battery and charging equipment chosen.
Traditional deep-cycle batteries are typically the least expensive, while AGM batteries are more expensive due to their superior performance and safety features.
Lithium batteries are the most expensive but offer longer lifespan and higher efficiency.
Additional costs include battery trays, isolators or DC-DC chargers, heavy-duty wiring, fuses and mounting hardware.
Higher-quality components are generally more expensive but offer better safety, durability and long-term value.
2. DIY vs Professional Installation
DIY installation can significantly reduce costs if the installer has basic electrical knowledge and the right tools.
Many vehicle owners prefer to install a second battery themselves for simple setups.
However, professional installation ensures expertise, proper wiring and adherence to safety standards.
Professional installation is recommended, specially for complex vehicles, lithium battery systems, or installations requiring custom mounting.
The choice between DIY and professional installation depends on skill level, time availability and the complexity of the system.
3. Time Required for Installation
The time required to install a second battery varies depending on experience and the type of setup.
A basic installation may take a few hours, while more complex systems with DC-DC chargers and custom wiring can take longer.
Professional installers typically complete the job faster due to their experience and specialized tools.
Taking sufficient time for proper installation ensures safety, correct charging and long-term reliability.
Conclusion – How to Install a Second Battery in a Car
When you add the dual battery setup to your vehicle, then it provides very reliable power without risking your engine starting power, so whenever the demand increases then a second battery becomes a necessity rather than an choice.
Now-a-days, the modern driving uses advanced lighting systems, electronic devices, work equipment and travel gear, a single starter battery is often insufficient to reliably meet these demands.
So, a properly installed dual battery system separates engine starting power from accessory power, protecting the main battery and ensuring reliable operation in all driving conditions.
And, by using the correct battery type, secure mounting, proper wiring, appropriate fusing and a reliable isolator or DC-DC charger, the system can charge efficiently without overloading the alternator or damaging electrical components.
At the end of the day, when you properly planned and installed, a dual battery system increases reliability, reduces electrical stress and provides dependable power, whether the vehicle is used for daily driving, long trips, work, or off-grid applications.
Now, that’s all from this guide and you can comment down below for more information related to this guide.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the main purpose of installing a second battery in a car?
Answer: The main purpose of installing a second battery is to power accessories without discharging the main starter battery. The starter battery is designed solely for starting the engine, not for powering devices for extended periods. A second battery allows you to safely run accessories such as lights, refrigerators, audio systems and chargers, while the engine battery remains fully charged and ready to start the vehicle.
Q2. Can a second battery damage my car’s electrical system?
Answer: If the second battery is installed correctly using proper wiring, fuses and an isolator or DC-DC charger, it will not damage the electrical system. Problems typically arise when the system is installed without proper protection or with incorrect wiring. A proper installation actually reduces stress on the electrical system by distributing the load more evenly.
Q3. Do I need a battery isolator for a second battery?
Answer: Yes, a battery isolator or DC-DC charger is essential for a safe dual battery setup. It prevents the second battery from discharging the starter battery when the engine is off. It also ensures that both batteries are properly charged when the engine is running. Without isolation, both batteries could discharge simultaneously, defeating the purpose of installing a second battery.
Q4. Can I install a second battery without professional help?
Answer: If a person has basic electrical knowledge, the right tools and carefully follows safety procedures, a second battery can be installed at home. Simple setups are often done as DIY projects. However, for complex systems, modern vehicles, lithium batteries, or when custom mounting and advanced wiring are required, professional installation is recommended.
Q5. Does a second battery affect fuel efficiency?
Answer: A second battery has very little impact on fuel efficiency during normal driving. The alternator already charges the main battery and charging a second battery only adds a small amount of load. Any impact on fuel consumption is minimal and usually negligible. The benefits of reliable power far outweigh this small difference.
Q6. How long does a second battery last?
Answer: The lifespan of a second battery depends on the battery type, usage and maintenance. Lead-acid and AGM batteries typically last several years with proper care, while lithium batteries can last considerably longer. Regular charging, avoiding excessive deep discharges and keeping the terminals clean helps extend battery life.
Q7. Can I use different types of batteries for the main and second battery?
Answer: Different types of batteries can be used, but only with the correct charging system. Mixing battery types without a DC-DC charger can lead to uneven charging and premature battery failure. Using the correct charger ensures each battery receives the appropriate voltage and charging profile, making mixed systems safe and reliable.
Q8. What is the safest place to install a second battery?
Answer: The safest location depends on the vehicle and battery type. Common locations include the engine bay, trunk, cargo area, or under the seats. The chosen location should provide secure mounting, protection from heat, adequate ventilation and easy access for maintenance. Sealed batteries are preferable for interior installations.
Q9. How do I know if my second battery is charging properly?
Answer: You can check charging by measuring the voltage with the engine running. The voltage should increase, indicating the alternator and charger are working. Accessories should operate smoothly without flickering or power loss. If the battery remains weak or doesn’t charge, there may be a problem with the wiring or charger.
Q10. Can a second battery drain the alternator?
Answer: When installed correctly, a second battery does not drain the alternator. The alternator is designed to handle the charging load within safe limits. Using the correct battery size and a proper isolator or DC-DC charger ensures that the alternator is not overloaded and operates efficiently.
Q11. Is it legal to install a second battery in a car?
Answer: In most places, installing a second battery is legal, provided it is installed safely and the wiring is secure. Some vehicles and commercial setups may have specific safety or inspection regulations. Using approved components and proper installation methods helps ensure compliance with local regulations.
Q12. Is a second battery beneficial for everyday driving?
Answer: For basic everyday driving with factory accessories, a second battery is usually not necessary. However, if the vehicle has additional electrical equipment or accessories that run even when parked, a second battery becomes very useful. It provides peace of mind and prevents the starter battery from being unexpectedly drained.
References:
[1] Optimized batteries for cars with dual electrical architecture
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/037877539402002K

Guys, I’m a car audio enthusiast and customization expert and I love clear sound and clean installation. Plus, I have spent years helping people build their dream audio setups. And whenever I’m working on cars, I probably listen to music and thinks about the next big upgrade.